A background check or background investigation is the process of looking up and compiling criminal records, commercial records and financial records (in certain instances such as employment screening) of an individual.
Background checks are often requested by employers on job candidates, especially on candidates seeking a position that requires high security or a position of trust, such as in a school, hospital, financial institution, airport, and government (including law enforcement and military). These checks are traditionally administered by a government agency for a nominal fee, but can also be administered by private companies. Results of a background check typically include past employment verification, credit score, and criminal history.
Background Check Types:
Fraud Checks
Employment Screening
Drug Testing
Criminal Record Checking
Background check international
Business intelligence investigations
Cross-border investigations
Legal support services
Insurance claims investigations
Landlord services
Reseller information consulting
Risk management consulting
Security consulting
Services security planning
Leading corporate security consultants, providing background checks, criminal records, company profiles, country info and online databases for the past twenty years to corporate, consulting firms, government departments, agencies, academic institutions etc., globally.
United Risk International, the leading corporate security consultants providing wholesale background checks, criminal records, reseller information
services, reports, company profiles, newsletters, country info and online databases for the past twenty years to corporate, consulting firms, government
departments, agencies, academic institutions etc., globally.
United-Risk.com is a company particularly for people who are looking for corporate, consulting firms, consulting services, corporate consulting
associates, agencies etc.
United Risk International is an independent, global risk consulting firm that helps you protect your human capital, reduce your exposure, and secure your
competitive edge.
Thursday, October 1, 2009
What is Background Check?
Wednesday, September 30, 2009
Ways for better quality link building
Link building is one of the most crucial parts of the SEO services. It is one of the essential things to be done to provide high search engine page ranking and improve the visibility of a website. It is however considered to be the backbone of the SEO services to bring in quality traffic to a website. It is the most efficient way to enhance the popularity of a website. Therefore it is necessary to ensure while going for link building that the web developer ensures you to get the facility of quality web content and business centric write ups and are backed by one way back links. It is also to be ensured that the website has a more professional look and is more users friendly for smoother web traffic. To have a quality link building exercise the placement of links has to be interrelated and voluntary. The thing is very simple that if you have a hair care website and that links to a web designing website and the web designing websites also link to a hair care or bodybuilding website. It will not give you a great value and moreover it does not make any sense.
One of the most common processes of link building is the directory submission. There are a number of free and paid directories available where you can submit your website. Some of the quality directories where you can submit your website are: www.dir.yahoo.com, www.avivadirectory.com, www.skaffe.com, www.joeant.com, www.wowdirectory.com, dmoz.org, www.goguides.com, www.gimpsy.com, etc. it is however recommended by the experts, never to use automated directory submission software. It is always better to be done manually. By doing that you are getting the chance of reading the guidelines before submission, which the automated softwares fail to do.
It is however known to all that article submission is perhaps the best way of gaining the maximum number of links. The best way of achieving it is to write quality contents and their submission. It is to be remembered to write original and quality articles relevant to content of your website and submit it to top article directories. This works as a great trick. The thing you can do is to write good quality and lengthy articles and place your website link below the content. It works great with the bloggers as they copy and paste your content on their website with your site link. The maximum number of time your article is copied the more links you are getting with each copy. For more traffic you can also donate articles with your site link to your blogger friends. A major trick is to keep half of the article on your site and the other half to the bloggers. In this way you can get more visitors to your site.
Another important method of link building is forum posting. By registering on different forums and participating in discussion there and using your site link as your signature is an awesome way of attracting more traffic towards your website.
Best online directories
Is well known that above all DMOZ directory is the best online directory. DMOZ, also known as The Open Directory Project (ODP), is a large, categorized directory of websites and pages, which is staffed by volunteers. Every website and page that is added to the directory has to be manually reviewed before it is included. Being listed in the directory is free.
But when you try to list your site in DMOZ you are in trouble. After you add your site an editor will approved it ... or not. And this can take months, even years.
So what is the solution ?
A good alternative until your site is listed to DMOZ is to submit your site to online free web directories. Submitting site to online free web directories will fast increase your PageRank. PageRank is an integral part of Google's ranking algorithm, and higher PageRank helps towards higher rankings. The PageRank within a website is increased by pages from other sites linking to it, and the higher the PageRank of the pages that link to it, the better it is for the receiving site.
When submitting a site to online free web directories, always take time to find the right category for it. Don't be tempted to submit it to a category that is higher up the tree than it belongs, because it won't be accepted there and, doing so, could cause unnecessary, self-induced delays. It does not matter the city in which you live – Atlanta, San Diego, Los Angeles or Washington – as you have access to information related to all those areas and even more. You can search for affordable places where you can purchase cars from, latest movies at the theater around the corner or the best restaurants in town.
Tips to Make Money in Network Marketing
What you probably didn't know then, was that being a distributor is going to take some business know how and a lot of marketing skills. This herein lies the problem. You, like most new people, may not have either. This leaves people like you with a garage full of products you couldn't even give away. That too takes some marketing skill.
Network marketing basically comes down to how fast you can move product. Without the proper skill set, it's going to be very challenging. Some people like to point the finger at the product or even the company as the reason they can't sell the product.
But if that was the case, then there wouldn't be any "heavy-hitters" in your company making money. Either they have mastered the art of marketing, or they're a "natural" at selling lots of products or have a bigger rolodex than you. You must have one of the three or your business could be heading for trouble, if it isn't already.
This leaves you in a dilemma. You either learn how to market your product or you go and try to recruit others to help you. Some go for the latter and find that it's difficult to recruit enough people into the business to make an impact in their bank account. This may your story too.
It's like you're stuck between two rocks...and neither of them is budging. The only way to make any headway is to saddle down and learn how to market; but not just market your products. You see, when you bring other people into your business, which you undoubtedly will sooner or later, they will have the same problems you had-not knowing how to market.
They will go through the very same dilemmas you went through and it will either break them or make them. More often than not, it does the latter. They will just quit your business because they couldn't figure it out fast enough to make a profit.
SEO India, seo services company india, seo services India, seo company India
Thursday, September 3, 2009
Membuat Status windows live messenger dengan PHP
status windows live messenger di websitenya dengan menggunakan icon buatan sendiri menggunakan PHP.
Untuk mendapatkan kode HTML untuk Windows Live Messenger IM Control,
login ke
http://settings.messenger.live.com/applications/websettings.aspx dengan
Windows Live ID Anda.
1.centang pada checbox "Allow anyine the internet ......"
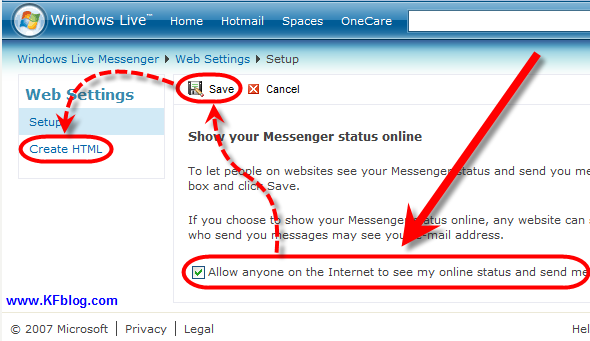
2. pilih menu create HTML
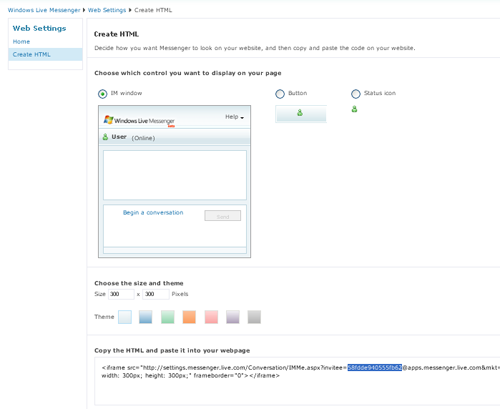
3. copy user ID
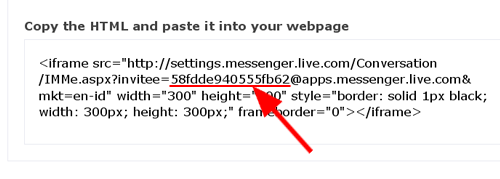
ini adalah contoh source yang sangat simple :
download here..
keterangan:
untuk memasang source status skype di atas, terlebih dahulu anda harus
membuat image aim_on.png dan aim_off.png (nama image bisa anda ganti
sesuai keinginan anda), dan $UserId= "58fdde940555fb62"; ganti dengan ID anda.
mudah - mudahan ini bisa mambantu....
Saturday, July 11, 2009
performance remains an uphill battle
This move is the latest volley in the rejuvenated browser wars, as browser vendors shift their focus toward improving the performance of Web-based applications. Google set the pace when it shipped Chrome with a high-performance JavaScript engine last year. Since then, Opera and Apple have both announced new JavaScript engines for their respective browsers, and even Microsoft has grudgingly worked to optimize IE8.
[ See also: Google seeks faster Web | Keep up with app dev issues and trends. Check out InfoWorld's Developer World channel and Fatal Exception and Strategic Developer blogs. ]
But browser performance isn't everything. Users experienced delays browsing major news sites in the wake of the death of pop star Michael Jackson last week, but the problem there wasn't slow browsers or even overloaded servers. According to Web monitoring company Keynote Systems, in many cases site slowdowns were caused by ad networks and other third-party content providers, whose own networks couldn't handle the increased traffic.
This incident underscores an issue of growing concern to Web developers. Modern Web apps typically draw from multiple content sources, data stores, and services, and growing interest in cloud computing will only accelerate this trend. But given all these interdependencies, can Web developers really guarantee fast, responsive user experiences? Or as the complexity of our applications continues to grow, is application performance gradually slipping out of our fingers? Are we all just throwing ourselves on the mercy of the Internet?
Web developers' cloud conundrum
Making Web pages is easy, but building efficient Web applications can be deceptively tricky. Desktop software is tangible; as a developer, you can get your hands around it. To optimize its performance, you do things like eliminating memory leaks and improving the efficiency of disk access. None of this applies to Web apps, however, where developers rely on browsers to handle local resources efficiently.
Instead, Web developers are confronted with the vagaries of the network. If a user accesses a Web page that draws images from a third-party provider, the overall user experience depends on the user's browser, the user's data connection, the outgoing pipe from the Web server, the Web application software, the pipe between the Web server and the image provider, and the image provider's server software. A Web application developer is in a position to optimize only one of these.
Consider what else developers take for granted in this distributed, cloud-based model. How can you be sure that the third-party image provider takes security seriously? How can you be sure that its systems are sufficiently redundant, and that it makes backups regularly, so you won't be blindsided by any unexpected outage? You can ask, of course.
A more immediate problem lies in the ways in which external services integrate with Web pages. Most of them rely on external JavaScript, iframes, or both. Either of these techniques can block a page's onLoad event, a major factor in the user's perception site slowness. This bottleneck happens before the JavaScript code executes, so the speed of the browser's JavaScript engine makes little difference. Combine this design with an overburdened network, and it's not just third-party content but your entire application that suffers.
Increased complexity leads to increased risk for Web apps
The Web community is working on ways to mitigate these problems. For example, modern browsers load other content elements while they're waiting for JavaScript to execute, and developers have come up with various clever techniques to eliminate script bottlenecks. But these one-sided optimizations can only get you so far, and they're difficult to do right.
"Think about it," says Steve Souter, a performance evangelist at Google and author of the books "High Performance Web Sites" and "Even Faster Web Sites." He adds, "We're taking a chunk of HTML that might also include CSS, JavaScript, and Flash, and stuffing it into another page ... It's not surprising that they can, and do, significantly degrade the performance of Web pages, and in some cases can cause a Web site to fail entirely."
Part of the problem lies in the fact that such content-integration efforts often lack cohesive management and oversight. "Integrating third-party content into a Web page would be a complex project to pull off for two teams working in the same company," Souter says. "In the case of ads, the two teams work at two different companies. In fact, the developers creating the ad probably never interact with the team building the main Web site."
That's not to say that everyone will share the responsibility for site slowdowns, however. Rest assured that when site performance degrades, the user will place the blame squarely on the site's own brand: The external content providers will remain virtually anonymous.
Baby steps toward the Web as a first-class app platform
For now, Web application developers and architects should be sure to educate themselves about the potential bottlenecks and other pitfalls inherent in distributed, cloud-like Web applications. Souter's books are a good place to start, and Google has recently launched a Web site dedicated to developing best practices for JavaScript performance.
In the long run, however, Web services providers and consumers will need to work together to develop standards of practice for the cloud-based Internet. The Interactive Advertising Bureau has formed a working group and offers best practices for ad providers to improve load times. This is a good start, but clearly there's still much more work to be done.
One of the more troubling aspects of the current situation is that it tends to favor larger customers. Wal-Mart or a major sports league might be in a position to demand comprehensive SLAs and developer accountability of their external content providers, but a struggling newspaper publisher might not -- to say nothing of even smaller clients.
That's why it's of critical importance that the Web community work to increase not just browser performance, but the performance of cross-organizational Web development teams. As sites and services become increasingly interconnected, we need to come up with new ways to communicate, collaborate, and cooperate to make distributed, cross-site development efforts run more smoothly. Only in this way will the cloud-based Web flourish into a reliable, first-class application development platform.
from : infoworld.com
Cloud computing made real
Not everyone is impressed with the search giant's latest move, however. My colleague Randall Kennedy says Chrome OS has "an ice cube's chance in Hell" of competing successfully with Windows or Mac OS X, citing the overwhelming effort needed to duplicate the full range of device drivers and applications available on those platforms today. Randall just doesn't see that happening, and for that matter neither do I.
[ Find out what InfoWorld contributors Randall Kennedy and Savio Rodrigues think of Google's newly announced OS ]
But Chrome OS isn't meant to be a pound-for-pound competitor to Windows. Though it's built on the Linux kernel, it's really something brand new. In fact, when we look back 10 years from now, the debut of Google's Chrome OS may well mark the moment when cloud computing finally became real.
Chrome OS: Custom-built for the cloud
It's particularly telling that Chrome OS will ship with support for both Intel and ARM processors. Google reps say the OS will initially target netbooks, and low-powered ARM chips are expected to play an increasing role in that market.
Even more interesting, however, is the revelation that the heart of the Chrome OS user experience is Google's Chrome browser -- and that booting a Chrome OS device should get you "onto the Web in seconds," according to the search giant's press release. In fact, the browser may be the only traditional application that runs on Chrome OS. Quoth the release: "For application developers, the Web is the platform" (emphasis mine).
This sounds an awful lot like the type of device I've talked about before, which I've dubbed "the Invisible PC." Rather than the traditional desktop model of applications running on a monolithic OS, in this new mode of computing the PC will all but disappear, leaving little more than a window to the Web. Desktop applications will be replaced by Web-based services, with computation and storage handled in the cloud.
It's fair to be skeptical, but don't underestimate the extent to which Web applications have already supplanted desktop software. Enterprises have been slow to adopt Web-based alternatives (and with good reason), but individual users have embraced them wholeheartedly. Remember when you had to install a special client program to read your e-mail? My mom doesn't. To her, e-mail is synonymous with Web-based services such as Gmail, MSN, and Yahoo Mail. Expect more categories of applications to go this way as Web technologies continue to mature.
Google isn't alone in pursuing the Invisible PC market, either. You could argue that devices like Nokia's Internet Tablet and the iPod Touch were the pioneers in this category, and Palm's WebOS shares Google's philosophy of Web-based application development. But Chrome OS promises a number of advantages that make it an ideal fit for today's lightweight netbooks and beyond.
The engine beneath the Chrome
For starters, Chrome is arguably the most technologically advanced browser in the world. Its multiprocess design, where each session exists independently from the others, more closely resembles a traditional OS than it does any other current browser, and its security model can't be beat. What's more, Chrome includes support for Google Gears, which gives it an advantage when Internet access is spotty.
As I mentioned before, Chrome OS runs on a Linux kernel, but that will hardly be relevant to application developers. Apps will be Web-based, but because the Chrome browser was designed with desktop PCs in mind, developers won't be limited to the stripped-down capabilities available in most smartphones and other devices. Google is one of the biggest advocates of the forthcoming HTML 5 specification, portions of which have already made their way into current-generation browsers, including Chrome. (And if you want to get an idea of the kind of applications made possible by HTML 5, look no further than Mozilla Bespin.)
Because Chrome OS is based on the open source Linux kernel, however -- and Google plans to open source the higher-level bits later this year -- the community will be free to lend a hand patching bugs and fixing security vulnerabilities as they appear.
Death to the desktop?
And there's more. Between the kernel and the Chrome interface, Google says it has developed "a new window manager" to handle rendering the GUI. Details are still scant, but from the sound of it, Google has opted to skip Gnome and KDE, and possibly even toss out the venerable X Window Manager itself. If so, Chrome OS is definitely not just another desktop Linux distro. In fact, it might not even qualify as a desktop OS at all.
How so? Consider how bloated mainstream desktops have become over the years. Whether your choice is Linux, Mac OS X, or Windows, your desktop greets you with countless menus, configuration panels, and applications, ranging from simple Internet clients to full-blown multimedia suites. Google's vision is different. "Google Chrome OS," Google's press release explains, "is being created for people who spend most of their time on the Web." If that's the case, then an old-style desktop is total overkill.
If your applications are Web-based, you don't need a software installer. Similarly, if all your data is stored in the cloud, the need for a full-featured file manager diminishes significantly, and you certainly won't need one of those fancy desktop search engines that are so much in vogue lately. You also won't need a backup manager, a disk defragmenter, a virus scanner, or a file-compression program. In fact, you probably don't need a desktop at all. What you'd really want is a lean, fast, responsive, simple UI -- something like you'd expect in a consumer electronics device -- and if Google is thinking like I'm thinking, expect Chrome OS to deliver just that.
Of course, we won't know what Chrome OS is really like until more details emerge later this year. But if it really is all that I think it could be, Chrome OS will bring changes to the PC market that have been a long time coming. We have a name for that: evolution.
from : infoworld.com
Blog Archive
Categories
- ADSENSE (3)
- Blogging (3)
- browsher (1)
- Building Traffic (12)
- Busby SEO Test (8)
- CSS (2)
- domain gratis (1)
- Free Domain (1)
- free hosting (2)
- Hardware amp; SoftWare (9)
- hosting (2)
- hosting gratis (2)
- HTML (3)
- Info Technology (8)
- Internet marketing (2)
- Link building (5)
- Search Engine Expert Directory (7)
- Search Engine Marketing (2)
- Search Engine Optimization (4)
- SEO (20)
- SEO Consulting (9)
- SEO For Auto Transporters (7)
- SEO Problems (4)
- Teknologi (12)
- tips (2)
- tips amp; trik (11)
- Tips and Tricks (4)
- tutorial (3)
- web directory (5)
- Webmaster and Search Events (3)
- Website Traffic (8)
- Yahoo Messenger (3)
Bloggerized by Free Blogger Template - Sponsored by Graphic ZONe and Technology Info